Complying with export compliance and international sanction laws has always been necessary, but the ongoing Ukraine-Russia Conflict has made these processes more complex and increasingly vital to protecting your business.
Over 8,000 sanctions are currently targeting Russian businesses and individuals, making Russia the most sanctioned country in the world. Fortunately, sanction screening solutions help organizations identify sanctioned parties within their supply chain and partnerships.
Additionally, new controls have been implemented that call for a renewed focus on export compliance. The right restricted party screening platform will also enable you to remain compliant with these new regulations, protecting you from fines and other penalties.
Why should you focus on sanction and export compliance? It’s because companies need to make sure that they are not entering into a business transaction with a denied party. Just one breach of export compliance regulations could result in a fine of potentially millions of dollars. There is a myth that compliance is complex and expensive. But that isn’t true. With robust denied party screening solutions, implementation is straightforward and costs start at several thousand dollars a year for a basic set up.
Today, we’ll break down some major stories in sanction and export control violations to highlight the importance of protecting your company.
Read on to learn why ensuring compliance with new regulations is a business imperative to consider as you prepare for the New Year.
2022 Sanction and Export Violations
Going over cases from the two main U.S. agencies involved with enforcing sanctions and export controls can help demonstrate the importance of staying compliant. Then, read through some of the top stories from 2022 to help refocus your efforts for the coming year.
Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) Incidents
OFAC is an intelligence and enforcement agency under the U.S. Treasury Department responsible for discovering sanction violations and imposing fines. In 2022, OFAC fined organizations a total of $38,284,196. Some of the significant cases are:
- A Washington-based rewards organization was fined $116,048 after violating several sanction programs. The company’s service lacked essential geolocation and restriction systems, allowing 27,720 rewards to be distributed to pirates within sanctioned nations.
- A U.S. cryptocurrency wallet service and exchange was fined $24.2 million, the most significant monetary penalty of the year. The company faced 116,421 sanction violations that fell under several sanction policies.
- An Australian-based logistics and freight company was fined US$6.1 million due to accepting payments through the U.S. financial system from sanctioned parties and countries. The company received the second-largest OFAC monetary penalty of 2022.
The lesson from all three cases is electronic transactions, whether rewards distribution or financial transactions, are being intensely scrutinized for sanction violations. If these organizations had the right tools in place, they would’ve been able to screen sanctioned entities, countries, and individuals to avoid these fines and reputation damage.
Bureau of Industry (BIS) Cases
BIS, an agency under the U.S. Department of Commerce, focuses on trade and commerce considered essential to national security. As a result, BIS has made significant indictments against those suspected of violating export restrictions. A few of the major cases in 2022 related to failing to comply with export controls include:
- Oil Traders Charged with Money Laundering and Sanctions Evasion: Oil traders and Russian nationals have been indicted with smuggling oil and money laundering in direct violation of export controls and sanctions. The indictment states that parties smuggled millions of oil barrels and tens of millions of dollars on behalf of Russian oligarchs. Defendants in the case are facing a maximum sentence of 30 years imprisonment.
- PJSC Lukoil Aircraft Export: The Russian multinational oil and gas corporation is charged with exporting U.S. aircraft from Dubai to Russia. The company did not seek an export license and violated export controls. The BIS has issued a seizure warrant for the aircraft.
- Attempted Smuggling by European Nationals: Two European nationals and other involved parties attempted to illegally export a dual-use high-precision jig grinder to Russia, which is export-controlled equipment. All involved parties are charged with conspiracy to violate international export controls. The indictment carries a maximum of five years in prison.
These indictments have penalties, including asset seizure and imprisonment. Comparatively, the OFAC fines discussed earlier were imposed on organizations that potentially inadvertently violated sanctions with financial transactions. These BIS indictments target seemingly intentional violations with significant criminal repercussions.
Global Context
Combined, both agencies have global reach by cooperating with allies in enforcing export controls and sanctions. The below graphic (see Figure 1) demonstrates this global scope; although it is not comprehensive, it highlights how international organizations can be penalized:
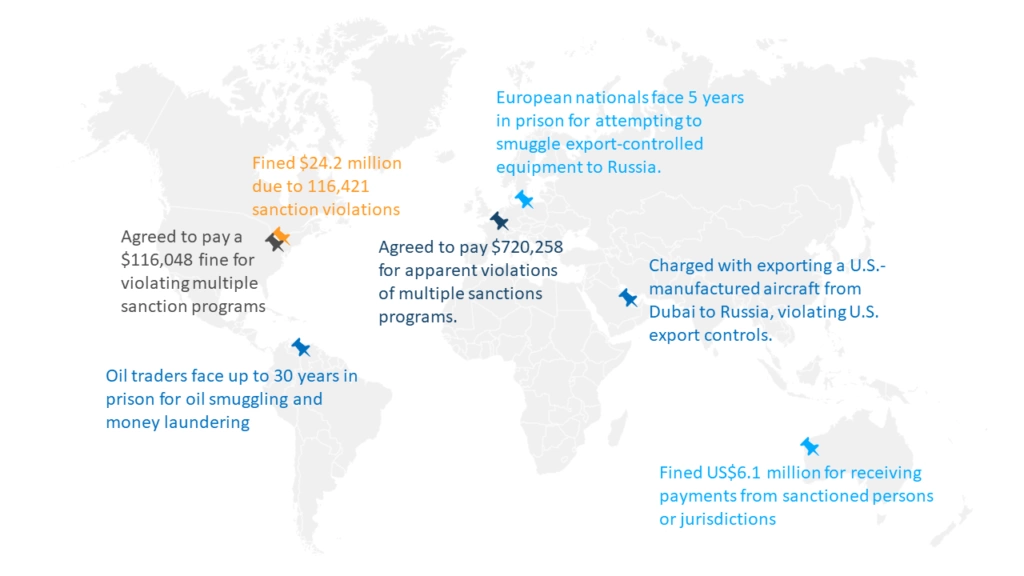
Figure 1: Major Export Compliance Violations in 2022
The United States and Allies Global Cooperation and Safeguards
The United States is working with its allies to identify, penalize, and charge all parties involved with violating sanctions and export controls. A recent speech from a leading BIS export enforcement agent highlights how the agency is working to make this happen.
Assistant Secretary for Export Enforcement Matthew S. Axelrod discussed how the United States and its allies are developing and enforcing export controls, stating, “Our domestic enforcement agents have reached out to almost 600 companies in the past six months to discuss our enhanced Russia controls.”
The United States is also working with regional governments to strengthen its efforts. For example, Axelrod explained, “We’ve also partnered with Singapore, Malaysia, and Japan to host the JIO (Joint Industry Outreach), which last year alone trained 1,400 exporters in the Asia-Pacific region on strategic trade controls more broadly.”
Compliance vs. Non-Compliance: What is the Real Cost?
Sanction compliance helps protect your organization against heavy fines and criminal charges. It’s clear that non-compliance can have steep fines and penalties, but will it cost to ensure compliance with export controls and sanctions?
While over 8,000 sanctions are currently in place and enforced on Russia, additional sanctions are likely. The chart, below, (see Figure 2) demonstrates sanction growth over the past few years.
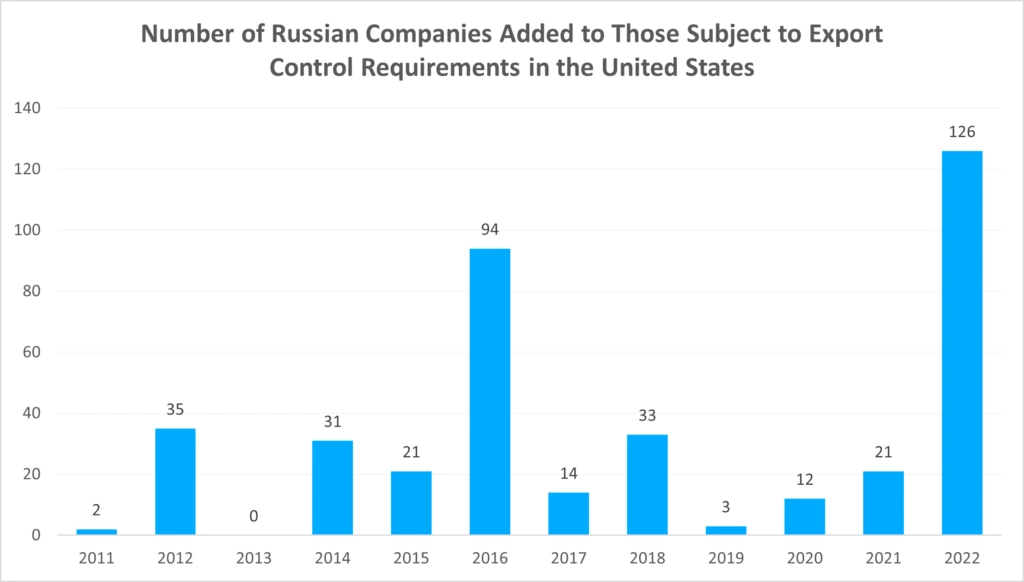
Figure 2: Russia export compliance sanctions growth 2011 to 2022
Source: Statista
The Immediate and Lasting Impact of Sanction and Export Violations
Identifying sanctioned parties within your existing partnerships and supply chain is the primary function of a denied party screening solution. What costs are involved if you decide not to use one? There are a few ways to evaluate the effect of a violation:
- Monetary fines
- Legal fees
- Operational disruption
- Damaged reputation and trust
- Detrimental effect on productivity
- Lost business opportunities
It can be challenging to quantify the actual cost of some of these effects, such as operational disruption and reputation damage. However, these long-term effects can have far-reaching effects on your business and growth potential.
Cost of Denied Party Screening
Protecting your business requires adopting the right tools and processes to conduct denied party screening. Restricted party screening is a specific process within export compliance that helps identify and remove any sanctioned parties you may be associated with.
Screening your partnerships for sanctioned entities is a monumental task if handled manually. Costs involved with manual screening will quickly add up, so it’s well worth embracing an automated platform to handle the heavy lifting.
So, what is the cost of a leading-edge restricted party screening solution? Costs will vary based on company size and the intricacy of the supply chain.
Simple implementations with one user and lower screening volumes will cost a few thousand dollars annually. An enterprise-level solution, however, can run to US$100,000 or more annually. Most companies should budget roughly US$20,000 for a denied party screening platform.
Additionally, sanctions and export controls include the OFAC’s 50 Percent Sanctioned Ownership Rule. This rule dictates that any entity with 50 percent or more ownership by sanctioned individuals is also considered sanctioned. The right sanction screening solutions will also guard against this rule, which is a significant challenge to handle manually.
Prepare for the New Year with Advanced Sanction and Export Compliance
Restrict party screening helps ensure sanction and export compliance, avoiding financial penalties and lasting consequences. As the New Year approaches, strengthen export compliance to keep your company protected.
Descartes Visual Compliance is a leading provider of denied party screening and export compliance solutions. Are you ready to discover how our solution can help? Reach out to our sanctions experts today to learn more.

